Ever stopped mid-sentence wondering, “Should I say giving or given?” You’re not alone. These two forms of the verb “give” confuse millions of English learners every year. The tricky part? Both are correct—just in different situations.
This guide breaks everything down in plain English. You’ll learn the difference between “giving” and “given”, how to use them in context, avoid common mistakes, and remember them forever with simple tricks.
Let’s dive right in.
Why “Giving” and “Given” Confuse So Many Learners
Both words come from the same root — “give.” The confusion begins because English verbs can change form depending on time (tense) and function (part of speech).
For example:
- I am giving a gift. → ongoing action
- I have given a gift. → completed action
At first glance, both look similar. But there’s a subtle difference in when and how the action happens. Once you see that pattern, the confusion disappears.
The Core Difference Between “Giving” and “Given”
Here’s the simplest way to think about it:
“Giving” = doing
“Given” = done
“Giving” shows an action in progress, while “given” shows something that has been completed or received.
Let’s make that clearer with a quick reference table.
| Form | Part of Speech | Function | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Giving | Present Participle | Shows ongoing action | She is giving her best. |
| Given | Past Participle / Adjective / Preposition | Shows completion or condition | The award was given to her. |
So, “giving” is active, “given” is result-oriented.
Understanding “Giving” in Continuous Tenses
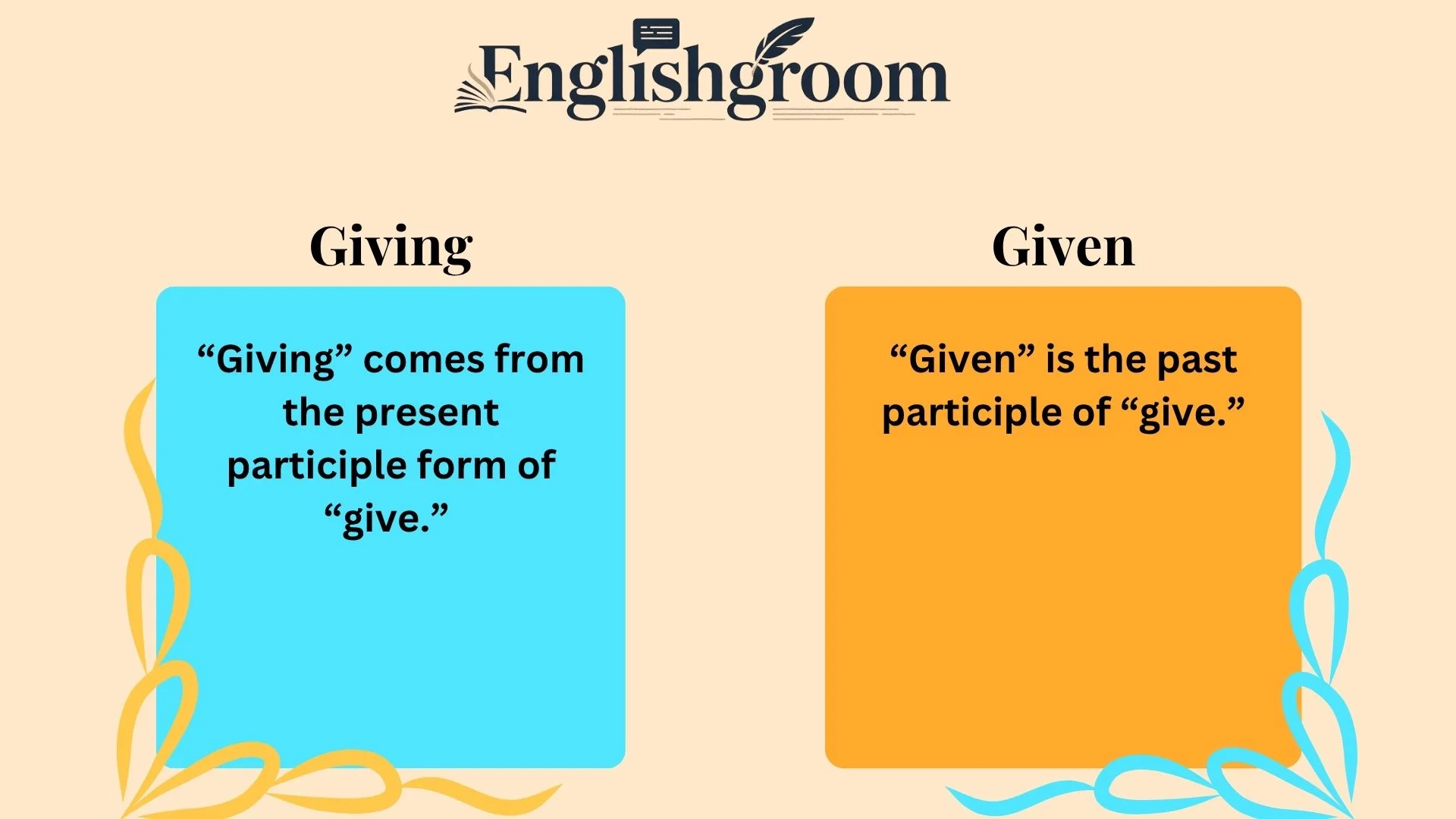
“Giving” comes from the present participle form of “give.” It’s used in continuous (progressive) tenses to express actions that are happening, were happening, or have been happening over time.
Present Continuous – Action Happening Now
The present continuous tense uses “am/is/are + giving.”
It describes something happening right now or around the present time.
Examples:
- I’m giving you my honest opinion.
- She’s giving her speech at the conference.
- They’re giving food to the people with low-income..
Usage Tips:
- Use it for actions in progress.
- Often appears with “now,” “currently,” or “at the moment.”
💡 Think of “giving” here as something still in motion.
Past Continuous – Action Happening in the Past
Formula: was/were + giving
It describes actions that were happening at a particular time in the past.
Examples:
- We were giving our best performance when the lights went out.
- He was giving his presentation when I arrived.
Key Point:
The focus is on interrupted or ongoing past activity.
🕒 Use “was giving” or “were giving” when the action was in progress at a specific past moment.
Present Perfect Continuous – Action Still in Progress
Formula: has/have been + giving
This tense shows an action that started in the past and is still continuing.
Examples:
- She has been giving piano lessons since 2018.
- They’ve been giving free samples all day.
Why It Matters:
This form emphasizes duration — how long something has been happening.
Common time markers: for, since, all day, recently, lately.
Common Mistakes with “Giving”
Even fluent speakers slip up. Here’s what to avoid:
| Mistake | Wrong Usage | Correct Usage |
|---|---|---|
| Mixing continuous with simple tenses | I give my speech now. | I am giving my speech now. |
| Using “giving” when the action is complete | She is giving her answer. (but she already did) | She has given her answer. |
| Adding “been giving” where not needed | He has been giving the prize yesterday. | He gave the prize yesterday. |
Quick Tip: If the action is over, don’t use “giving.” Use “given” instead.
The Versatility of “Given”
“Given” is the past participle of “give.” It’s used to show completed actions, passive constructions, or even as an adjective and preposition.
Let’s explore its many roles.
“Given” as a Past Participle in Perfect Tenses
Formula: has/have/had + given
Used to show an action that’s finished, completed, or has relevance to the present.
Examples:
- She has given her word.
- They had given everything before quitting.
- He’s given his time to charity for years.
Why It’s Important:
The past participle connects past actions to present consequences.
Compare:
- I give → present
- I am giving → now
- I have given → completed action
“Given” in Passive Voice
Formula: be + given
Used when the receiver of the action is more important than the doer.
Examples:
- The prize was given to the winner.
- Instructions were given before the test.
- A second chance will be given to all applicants.
Tip:
Passive voice emphasizes what was done, not who did it.
🗣️ “Given” often appears in formal or official writing.
“Given” as an Adjective
“Given” can describe something assumed, accepted, or specific.
Examples:
- At any given time, 200 users are online.
- It’s a given fact that water boils at 100°C.
- The given data shows an increase in sales.
Meaning:
Here, “given” means particular, fixed, or certain.
Grammar Note:
When “given” acts as an adjective, it modifies a noun, just like “known,” “expected,” or “assumed.”
“Given” as a Preposition
This one surprises many learners.
“Given” can mean considering or because of.
Examples:
- Given the weather, the match was postponed.
- Given her experience, she’ll handle it well.
- Given the circumstances, we had to act fast.
Usage Tip:
This is common in formal or written English. Replace “given” with “considering” and the meaning stays the same.
✏️ “Given the time,” means “Considering the time.”
Comparing “Giving” vs “Given” in Real Contexts
Sometimes, the easiest way to understand grammar is to see it in action.
Here’s a side-by-side comparison to make things crystal clear:
| Sentence | Correct Form | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| She is ___ her time to charity. | giving | Ongoing action |
| She has ___ her time to charity. | given | Action completed |
| The teacher is ___ homework today. | giving | Still happening |
| The teacher has ___ homework already. | given | Done earlier |
| At any ___ time, the team is busy. | given | Used as an adjective |
| ___ the situation, we’ll leave early. | Given | Used as a preposition |
Remember:
If it’s happening now or still continuing, use giving.
If it’s already finished or assumed, use given.
How to Choose Between “Giving” and “Given”
Here’s a simple test to help you decide fast:
- Is the action happening right now or continuing?
→ Use “giving.” - Is the action completed or referring to something that already happened?
→ Use “given.” - Is it describing a condition, assumption, or prepositional phrase?
→ Use “given.”
Visual Decision Tree
Is the action still happening?
│
├── Yes → Use “Giving”
│ (She is giving a speech)
│
└── No → Is the action completed?
│
├── Yes → Use “Given”
│ (She has given her speech)
│
└── Is it a condition/preposition?
│
└── Yes → Use “Given”
(Given the time, we left)
Mnemonics and Memory Tricks
Here’s how to remember the difference without overthinking:
- “Giving = Doing” (still happening)
- “Given = Done” (already finished)
Quick Rhymes
“If it’s in motion, use ‘giving.’
If it’s complete, ‘given’ is fitting.”
Analogy
Think of “give” like handing over a gift.
- While you’re handing it → you’re giving it.
- Once it’s in their hands → it’s given.
Common Errors and Fixes
Here are some real-world mix-ups and how to correct them.
| Mistake | Incorrect | Correct | Why |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mixing tenses | I am given a gift now. | I am giving a gift now. | “Given” can’t follow “am” for active voice. |
| Using “giving” after “has/have” | She has been giving her answer. (completed) | She has given her answer. | Use “given” for finished actions. |
| Confusing adjective use | At any giving time… | At any given time… | “Given” describes a condition, not “giving.” |
🔍 Tip: “Given” never pairs with “am/is/are” in active voice sentences.
Practice Section: Test Your Understanding
Try these. Fill in the blanks with giving or given.
- She is ___ a talk on global warming.
- He has ___ all he could to help.
- The prize was ___ to the best student.
- They are ___ their time to the project.
- ___ the weather, we’ll stay inside.
Answers:
- giving
- given
- given
- giving
- given
🎯 If you got them all right, you’ve nailed it!
Case Study: “Giving” vs “Given” in Real Speech
Let’s look at a real-life scenario.
Situation:
You’re explaining your volunteer work.
- Incorrect: “I have been giving food yesterday.”
- Correct: “I gave food yesterday.” OR “I have given food to the people with low-income many times.”
Why?
“Yesterday” refers to a completed past action, so “given” (or “gave”) fits better than “giving.”
Another one:
- Correct: “I am giving my best to finish this project.”
Here, the action is still in progress, so “giving” is the right call.

FAQs: Common Questions About “Giving” and “Given”
What’s the main difference between “giving” and “given”?
“Giving” shows an ongoing action. “Given” shows a completed one or describes a condition.
Can I use “given” at the start of a sentence?
Yes. For example: “Given the circumstances, we acted fast.” It means considering the circumstances.
Is “given” past tense?
Not exactly. It’s a past participle, which works with helping verbs like has/have/had.
Can I say “I am given”?
Only in passive voice. Example: “I am given tasks daily.” It means someone assigns tasks to me.
What’s a quick way to remember the rule?
Think: “Giving = doing,” “Given = done.” If it’s happening → giving; if it’s finished → given.
Learn More English With These Best Articles:
Sorry for Bothering You vs Sorry to Bother You The Subtle Difference That Changes Everything
Is It Correct to Say It Was a Pleasure Meeting You? A Complete Guide to Using It Naturally and Professionally
Mastering Having vs Having Had in English Grammar
Mine as Well or Might as Well? The Ultimate Guide to Getting It Right
To Fast or Too Fast? Mastering One of English’s Most Confusing Grammar Rules
Conclusion
You’ve now seen the full picture. “Giving” represents an action in progress, while “given” reflects something completed, received, or assumed.
To recap:
- Giving = Continuous, ongoing
- Given = Completed or descriptive
- Use “given” as a preposition or adjective when describing conditions
Next time you hesitate, ask yourself one question: Is the action still happening?
If yes, say “giving.” If no, go with “given.”
“Once you grasp the timeline, the choice becomes effortless.”
Keep practicing, and soon, choosing between “giving” and “given” will feel as natural as saying hello.

Hi! I’m Sami, a 28-year-old content writer with a love for words and storytelling. Writing has always been my way of expressing ideas, sharing knowledge, and connecting with people. I enjoy creating engaging and well-researched content—whether it’s blogs, articles, or social media posts—that not only informs but also inspires readers. My goal is to turn complex ideas into clear, creative, and meaningful pieces of writing that leave a lasting impact.



